Brain Arrhythmia
You may have heard of a heart arrhythmia, or an irregular heartbeat pattern. Similarly, a brain arrhythmia is an irregular or disrupted brainwave pattern.
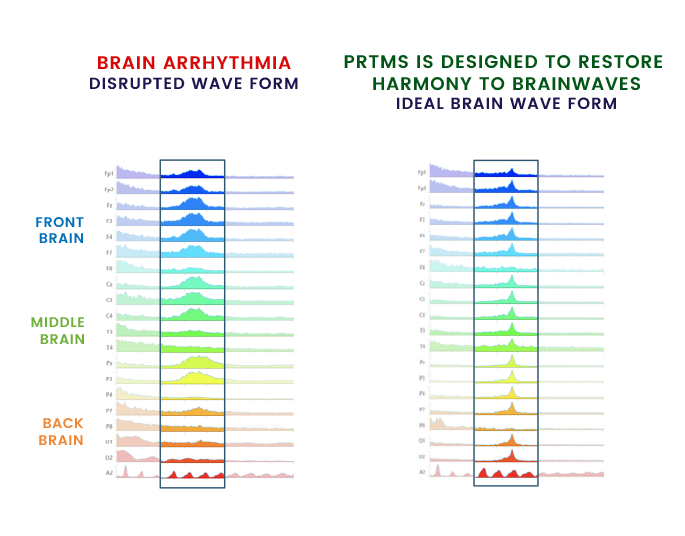
These disruptions in brainwave activity then manifest outwardly into daily neurocognitive symptoms.Brain arrhythmia is believed by some to be at the root of many mental conditions — such as depression, anxiety, PTSD, OCD, sleep disorders, migraine, addiction, ADD/ADHD, autism, and more.
But what makes brainwaves qualify as “disrupted”?
To understand this, we must first take a look at the basics of human brainwave activity. Brainwave frequencies are measured in Hertz (Hz) and depending on what frequency your brain is operating at, you feel different levels of alertness. For example, if your brain is operating at Delta speed (0.1-3 Hz), you are most likely sleeping. If you are operating at Gamma speed (31-100 Hz) you are experiencing the highest level of alertness and more than likely in a situation that requires it. But the frequency we are most interested in is our Alpha frequency. This ranges from 8-12 Hertz and is the state in which the mind is awake, but relaxed. We focus on this resting state because, ideally, 80% of our waking hours are spent there.
In the simplest terms, brainwaves are disrupted when they become out of sync with one another. This can be depicted above as a flattened peak, multiple peaks, and/or a vast range of other discrepancies in wave formation – which all may mean very different things.

